GPU Partition
The GPU partition is comprised of 4 nodes with a total of 32 H200 GPUs. This page guides users on how to access and utilize the H200 GPUs using slurm and Open OnDemand.
Using H200 GPUs on Open OnDemand
NCShare users can access H200 GPUs through Open OnDemand containers such as Jupyter Lab. A few of these Apptainer containers have been built with GPU support.
Once logged into Open OnDemand, you can select your desired container (e.g., Jupter Lab, RStudio etc.).
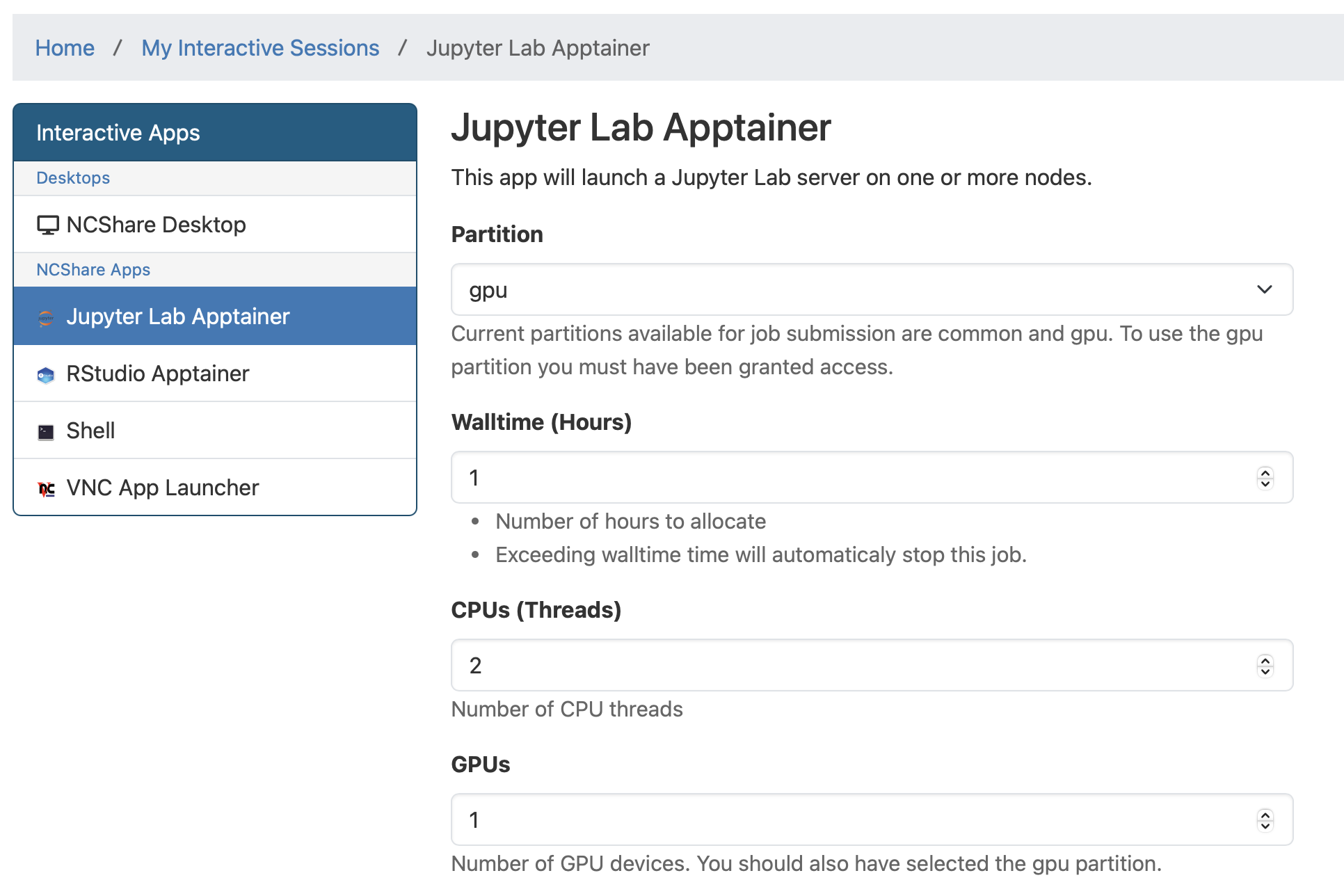
If you select Jupyter Lab, you will be taken to the Jupyter Lab Apptainer page where you should select gpu under Partition and specify the number of GPUs you wish to use under GPUs. Then click Launch.
To verify if the notebook has connected to a GPU, you can run the following code that imports and runs a few PyTorch functions in a notebook cell:
import torch
print("torch:", torch.__version__)
print("torch.version.cuda:", torch.version.cuda)
print("torch.cuda.device_count():", torch.cuda.device_count())
print("torch.cuda.is_available():", torch.cuda.is_available())
If the cell execution shows an output similar to the following, Congratulations!, you have successfully connected to an H200 GPU!
torch: 2.8.0+cu128
torch.version.cuda: 12.8
torch.cuda.device_count(): 1
torch.cuda.is_available(): True
Using H200 GPUs with slurm
First, ensure that you are able to ssh into a NCShare login node from a terminal following the instructions given in the Register an ssh key guide.
Once, you have access to a login node, you will use the following slurm flags to request H200 GPUs for your job.
-A, --account=<institution>_h200
-p, --partition=gpu
--gres=gpu:h200:N
where <institution> is your institution ID (e.g., ncsu, duke, etc.) and N is the number of GPUs you wish to request.
Information about the GPU partition is given below. Institution names are listed in the AllowGroups field.
(base) kkilroy2@login-01:~$ scontrol show partition gpu
PartitionName=gpu
AllowGroups=appstate_h200,campbell_h200,catawba_h200,charlotte_h200,chowan_h200,davidson_h200,duke_h200,ecu_h200,elon_h200,fsu_h200,guilford_h200,meredith_h200,ncat_h200,nccu_h200,ncssm_h200,ncsu_h200,uncp_h200,uncw_h200,unc_h200,wfu_h200,wssu_h200 AllowAccounts=ALL AllowQos=ALL
AllocNodes=ALL Default=NO QoS=N/A
DefaultTime=NONE DisableRootJobs=NO ExclusiveUser=NO ExclusiveTopo=NO GraceTime=0 Hidden=NO
MaxNodes=UNLIMITED MaxTime=2-00:00:00 MinNodes=0 LLN=NO MaxCPUsPerNode=UNLIMITED MaxCPUsPerSocket=UNLIMITED
Nodes=compute-gpu-[01-04]
PriorityJobFactor=30 PriorityTier=30 RootOnly=NO ReqResv=NO OverSubscribe=NO
OverTimeLimit=NONE PreemptMode=OFF
State=UP TotalCPUs=768 TotalNodes=4 SelectTypeParameters=NONE
JobDefaults=(null)
DefMemPerNode=UNLIMITED MaxMemPerNode=UNLIMITED
TRES=cpu=768,mem=8255656M,node=4,billing=768,gres/gpu=32
Interactive GPU Session
To obtain an interactive GPU session, you can use the following command from a login node,
srun -A duke -p gpu --gres=gpu:h200:1 -t 1:00:00 --pty bash -i
This requests 1 H200 GPU for 1 hour on the gpu partition under the duke account. To obtain information about your allocated GPU, you can run the nvidia-smi command once inside the interactive session.
(base) uherathmudiyanselage1 at compute-gpu-02 in /work/uherathmudiyanselage1
$ nvidia-smi
Mon Nov 3 07:48:27 2025
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| NVIDIA-SMI 570.172.08 Driver Version: 570.172.08 CUDA Version: 12.8 |
|-----------------------------------------+------------------------+----------------------+
| GPU Name Persistence-M | Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC |
| Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap | Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. |
| | | MIG M. |
|=========================================+========================+======================|
| 0 NVIDIA H200 On | 00000000:4B:00.0 Off | 0 |
| N/A 31C P0 74W / 700W | 0MiB / 143771MiB | 0% Default |
| | | Disabled |
+-----------------------------------------+------------------------+----------------------+
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Processes: |
| GPU GI CI PID Type Process name GPU Memory |
| ID ID Usage |
|=========================================================================================|
| No running processes found |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
You can run your GPU tasks inside this interactive session. Once done, you can exit the session by typing exit or pressing Ctrl+D.
slurm Batch Job Submission
For computationally intensive tasks, it is recommended to submit a batch job using a slurm job script. Below is an example slurm job script that requests 1 H200 GPU for 1 hour.
jobscript.sh:
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -J name_of_job
#SBATCH -p gpu
#SBATCH --gres=gpu:h200:1
#SBATCH --account=duke
#SBATCH -t 1:00:00
# Initialization
source ~/.bashrc
cd $SLURM_SUBMIT_DIR
cat << EOF > compute-gpu-01.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
import torch
print("torch:", torch.__version__)
print("torch.version.cuda:", torch.version.cuda)
print("torch.cuda.device_count():", torch.cuda.device_count())
print("torch.cuda.is_available():", torch.cuda.is_available())
EOF
chmod +x compute-gpu-01.py
./compute-gpu-01.py > compute-gpu-01.log
For advanced users who are running computationally intensive jobs, the following additional optional flags might be useful,
#SBATCH -N 1 # Total no. of nodes
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node 96 # Tasks per node
#SBATCH -c 2 # CPUs per task
#SBATCH --mem=500G # Memory per node
To submit the job script, use the following command from a login node:
sbatch jobscript.sh
You can monitor the status of your job using the squeue command:
squeue -u $USER